LAB : git, gdb
LAB : git, gdb
How to use Terminal
Retrieve file on current directory
$ ls
Current Location
$ pwd
Directory Type
- Normal directory : <dir-name>
- Current directory : .
- Parent directory : ..
- Root directory : /
- Home directory : ~
Path type
- Absolute address : /<dir1>/<dir2> ..
- Relative address: : <dir1>/<dir2>
Make directory
$ mkdir <dir-name>
Change the shell working directory
$ cd <destination directory>
Remove
$ rm <file-name>
$ rm -rf <dir-name>
Move source(s) to destination directory
$ mv <source file> <destination directory>
$ mv <source directory> <destination directory>
Rename SOURCE to DEST
$ mv <SOURCE> <DEST>
Copy
$ cp <source file> <destination directory>
$ cp <source file> <destination file>
$ cp -r <source directory> <destination directory>
Git workflow overview
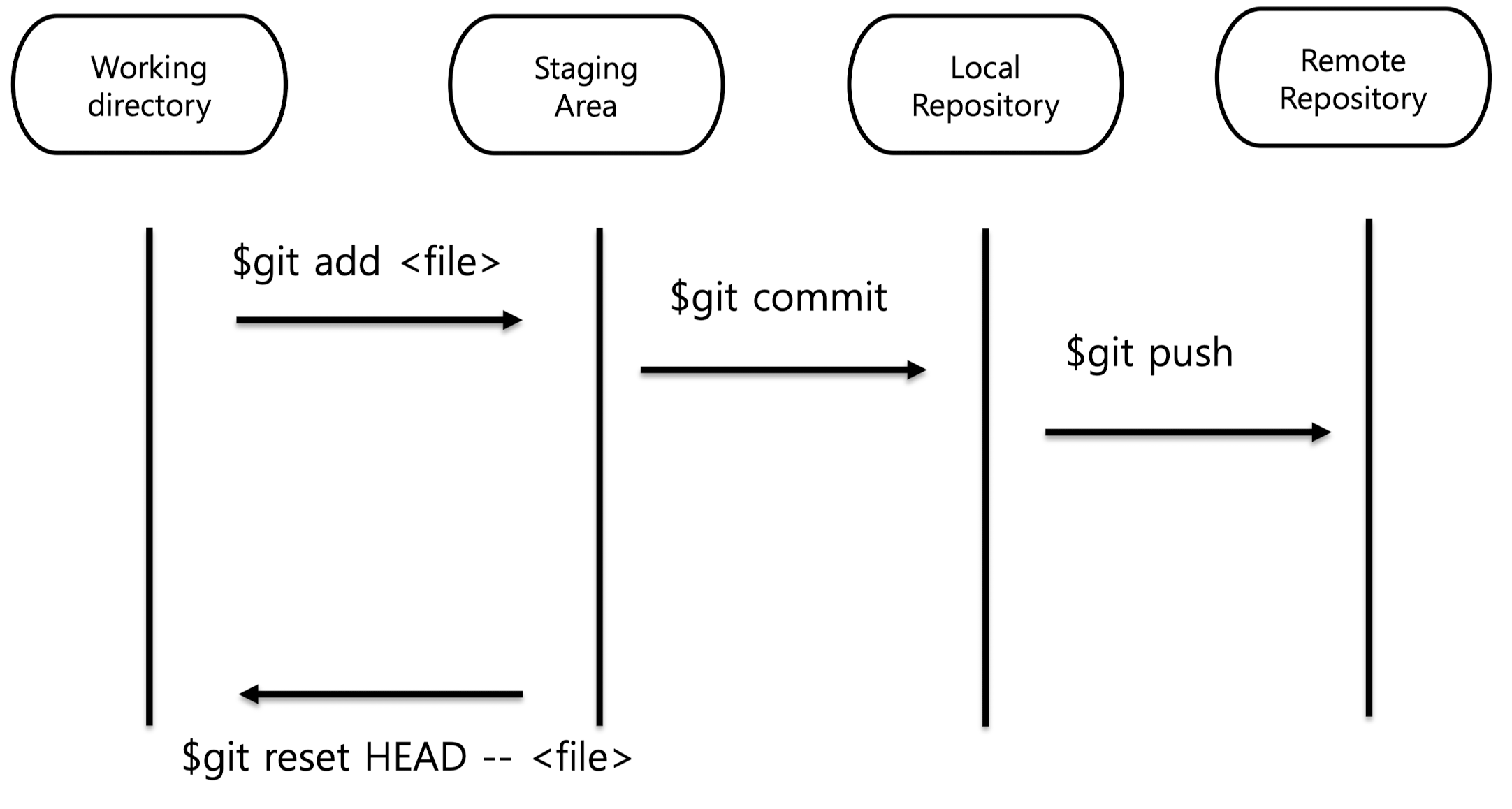
Staging Area : 버전 관리에 등록, 파일 목록만 관리, 내용은 올리지 않음
Local Repository : 수정된 내용까지 현재 버전이 copy가 됨
fetch : 커밋된 내용들을 local repository로 받아옴 (다운로드)
merge : local repository에 있는 내용을 working directory까지 가져옴 (병합해줌)
pull : fetch와 merge를 한번에 하는 것
checkout : working directory의 변경사항을 버리고 가장 최근 local repository의 backup으로 덮어쓰고 싶을 때 씀
Git : staging
$ git status
현재 staging area에서 관리되고 있는 파일 중에 변경내용과, 관리되지 않고 있는 파일들을 보여줌
$ git add * // 현재 디렉토리에 있는 변경된 파일만 스테이징
$ git add . // 현재 디렉토리와 그 하위 디렉토리에 있는 모든 변경된 파일을 스테이징 영역에 추가
Git : unstaging
$ git reset HEAD -- <file>
관리하고 싶지 않은 파일 (ex. 실행파일) 들을 staging area에서 빼줌
Git : commit
$ git commit -m "commit message"
커밋을 할 때는 메시지를 적어주어 무엇을 변경했는지 알림
$ git log
모든 커밋 내용을 볼 수 있음
Git : push
$ git push
What is G++
g++ : open-sourced C++ compiler
g++ [options] <infile> …
- -c : compile and assemble, but do not link Create only object file (.o) without creating executable
- -g : debug info. Contains information necessary for debugging (source code, etc.)
- -o <outfile> : Place the output into <outfile>
- -I <dir> : include directory. (directory name to look for headers when compiling)
- -L <dir> : library directory. (Directory name to look for library files when linking)
- -D <symbol>[=def] : define a macro to use at compile time
- … : There are numerous other options.
Example : Compile & Link
compile and link the two source file (main.cc, print.cc)
$ g++ -c -o main.o main.cc
$ g++ -c -o print.o print.cc
$ g++ -o hello_world main.o print.o
shortcut
$ g++ -o hello_world main.cc print.cc
Run
$ ./hello_world
Make
Make : Build tools that have been around for a long time on Unix operating systems
- 실행파일을 만들 때의 규칙들을 저장해놓고, make하면 필요한 파일만 변경해줌
Makefile
How to write Makefile
target: prerequisites
<TAB>command1
<TAB>command2
Example
hello_world: main.o print.o
g++ -o hello_world main.o print.o
main.o: main.cc
g++ -c main.cc
print.o: print.cc
g++ -c print.cc
clean:
rm hello_world main.o print.o
Execute makefile (1) : generate executable file
$ make
Execute makefile (2) : Remove Excutable file and All object files
$ make clean
GDB
디버깅 툴, 프로그램 build할 때 -g option 줘야됨
gdb [options] <command>
<command> : If the current directory is not in your PATH, you must include ./.
Basic command
r [arguments] : Run the given command.
– bt : backtrack. Show current call stack status.
– up/down [steps] : Move up / down a given step from the current position of the call stack.
– p <variable> : Display the value of a given variable.
– q : exit gdb process.
– Use more easy-to-use improved programs such as cgdb and ddd
– s : step in (함수로 따라 들어감)
– n : next